BMWi-project: Kläffizient
BMWi-project: Kläffizient – Flexible and demand-oriented refinement of sewage gas for energy storage and increased plant efficiency
The BMWi project “Kläffizient” (“Sewage Efficient”) investigates the potential of sewage treatment plants as so-called “prosumers”, i.e. as producers and consumers of electricity, biomethane and heat on the increasingly decentralised and flexible energy market both in simulations and experiments.
Support Code: 03EI5421A
Term: 01.10.2020 – 30.09.2023

Energetische Nutzung biogener Rest- und Abfallstoffe
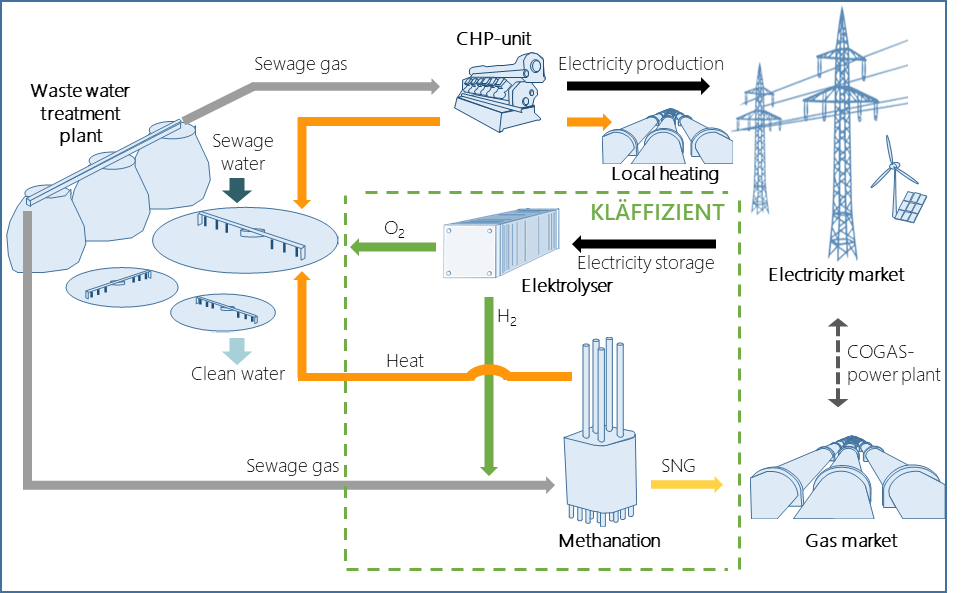
The project Kläffizient (“Sewage Efficient”) investigates the flexibilisation of sewage treatment plants towards players on energy markets. Conventional wastewater treatment plants are mainly designed to minimise energy costs. However, biomethane can be fed into the gas market via sewage gas refinement. Strong synergies can be utilised, such as the parallel use of the electrolysis products hydrogen (as an educt gas for subsequent methanation) and oxygen for aeration of the biological stage. The concept of sewage gas refinement opens up a wide horizon of flexibility, where different operating and marketing strategies can be economically viable. For this reason, an optimised operating mode for waste water treatment plants using varying energy price scenarios is to be found with a system-dynamically modelled “digital twin”.
The aim of the project is to test the flexible methanation of sewage gas in a varying energy market. In addition to simulative observations, demonstrations of methanation will be carried out at a waste water treatment plant site. In this way, a contribution to climate protection is to be made while at the same time optimising the operating costs of waste water treatment plants.
Contact:
Department of Chemical and Biological EngineeringJonas Miederer, M. Sc.
Lehrstuhl für Energieverfahrenstechnik



